|
Suicidal ideation less prevalent in strong men
The more muscle strength men have, the less often they think about suicide. American epidemiologists come to this conclusion in a study published in the Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports.
Study
The researchers, who were affiliated with Washington University School of Medicine, used data from nearly 9,000 adults collected in 2011 and 2014 in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey ([HANES].
The study participants had squeezed a gripper that registered the maximum strength that the participants were able to develop. The participants also shared how many times in the past two weeks they had thought they would be better off dead, or had considered to seriously injure themselves.
Results
The researchers found no significant association between muscle strength and suicidal ideation in women, but they did in men. For every extra 5 kilos of strength with which the men could squeeze a gripper, the chance of suicidal ideation decreased by 16 percent.
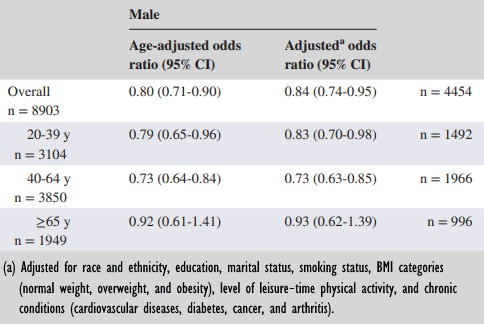
When the researchers split their data by age group, they saw that the association no longer was significant in men who had passed the age of 65.
Conclusion
"Monitoring handgrip strength may be important to identify men with suicidal ideation or thoughts", the researchers conclude. "Our study also provides novel strategies which may help prevent suicidal ideation in males by improving physical functioning through strength training activities."
Help
Are you thinking about suicide? Get help. Call a suicide hotline. [Click here]
Source:
Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020 Jan;30(1):92-9.
More:
Women prefer men with strong hands 06.12.2018
Archives:
Fighting Depression
Strength Training
Psychology
|