|
Why moderate continuous activity is a better antidepressant than HIT
Exercise is an effective remedy for depression, but not all forms of exercise are equally suitable as an anti-depressant. Both high- and moderate-intensity exercise dispel the gloom, but high-intensity exercise also appears to cause more stress.
Study
In 2018, Canadian kinesiologists from McMaster published a human study in which 61 students participated as test subjects. The researchers divided the students into 3 groups.

The students in the control group [CON] did nothing for 6 weeks.
The subjects in a second group cycled 3 times a week for just under half an hour at 40 percent of their maximum [moderate continuous training; MCT].
The students in a third group did high-intensity training [high-intensity interval training; HIT] that required the same amount of energy as the moderate-intensity workout. The HIT training consisted of 10 1-minute sprints in which the students cycled at 80 percent of their maximum. Between the sprints, the students cycled at a leisurely pace. Each HIT workout lasted 20 minutes.
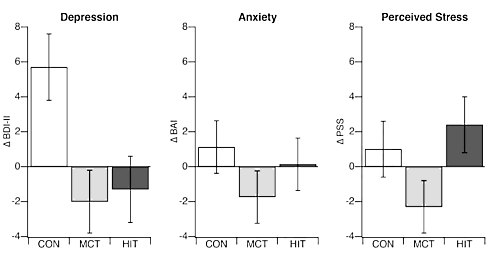
Before and after the 6 weeks, the Canadians used questionnaires to determine how much the students suffered from depressive symptoms, anxiety and stress in their daily lives.
Results
Both the moderate-intensity exercise and the high-intensity exercise reduced depressive symptoms. The high-intensity training caused more stress, the moderate-intensity training did not.
Mechanism
Both the moderate-intensity exercise and the high-intensity exercise reduced depressive symptoms. The high-intensity training caused more stress, the moderate-intensity training did not.
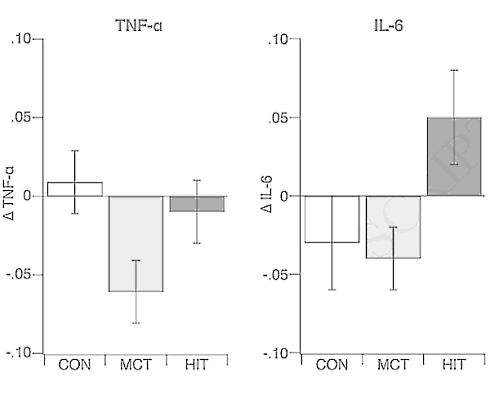
The Canadians suspect that this increase in interleukin-6 activity and decrease in TNF-alpha explain why the students in the moderate-intensity exercise group had started to feel better, while the students in the high-intensity exercise group did not.
Conclusion
"Taken together the results suggest that moderate-intensity exercise may be an optimal intensity for promoting mental health", write the researchers.
Source:
Biol Psychol. 2018 Mar;133:79-84.
More:
Depression disappears faster due to less than an hour of strength training or cardio per week 16.11.2019
Intensive weight training helps fight depression 05.06.2013
Archives:
Cardio Training
Psychology
Depression
 |
 |
 |
|
St. John's wort reduces depression | Meta-study
St John's wort really works against depression. This is evident from a meta-study that combined and re-analyzed data from three dozen previously published trials.
|
SAMe mitigates major depression
Supplementing with S-adenosyl-methionine, commonly abbreviated as SAMe, improves mood, according to the supplement industry. According to an Italian review study, this may well be true.
|
EPA is an antidepressant
Curcumin may be just as effective an antidepressant as fluoxetine, we reported not long ago. Well, what curcumin can do, EPA can do too.
|
|






