Study
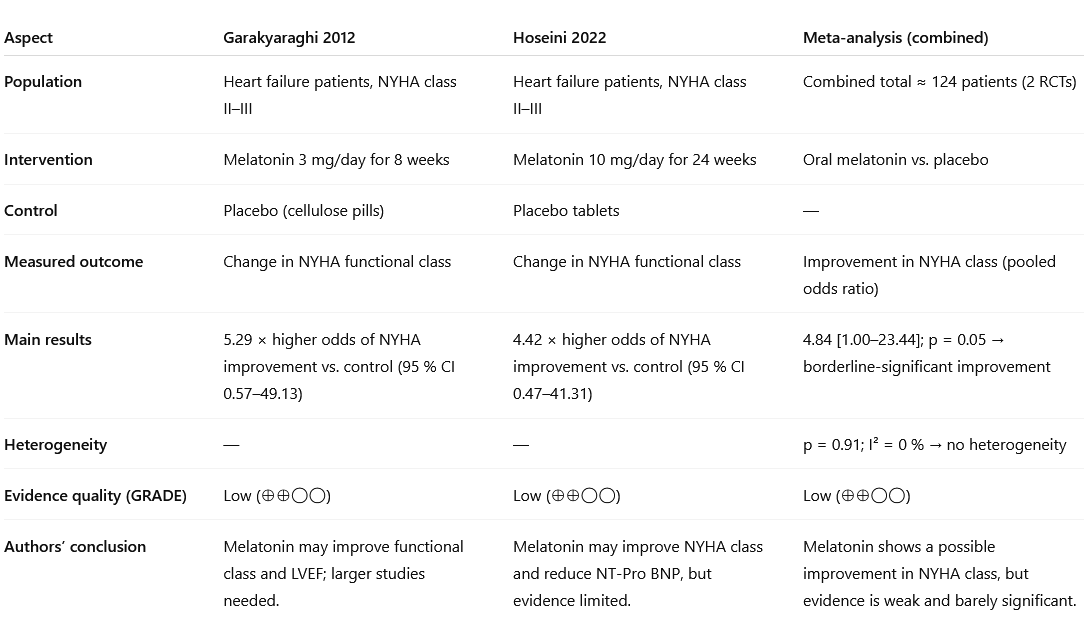
The participants took their supplements 30 to 60 minutes before bed. Doses ranged from 3 to 20 milligrams per day, and the trials lasted 8 to 24 weeks.
The participants were diagnosed with a form of heart failure in which they noticed their heart function was impaired during exercise, but not yet during rest. Their heart failure had a score of NYHA-2 or NYHA-3. NYHA stands for New York Heart Association [NYHA] Functional Class.
The researchers pooled the results from the trials and reanalyzed them.
Results
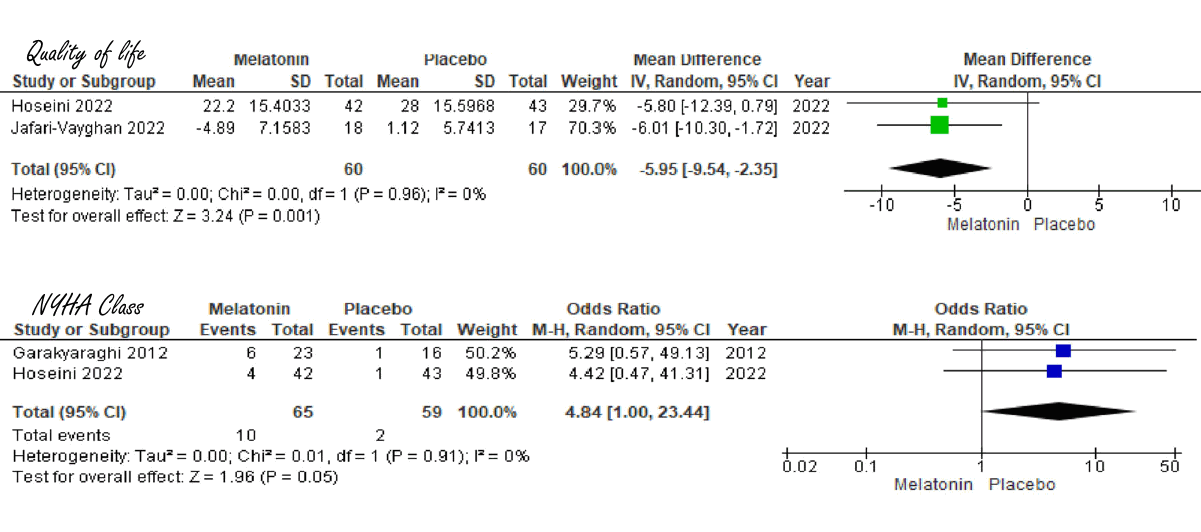
Two trials assessed the effect of melatonin supplementation on quality of life (QoL). When participants had to rate their QoL, it increased from a 7.2 to a 7.8. The effect was statistically and clinically significant.
This was partly because the supplementation improved sleep, reduced daytime fatigue, and increased appetite.
According to statistical analyses, the effect on the severity of heart failure was right on the borderline between significance and non-significance. In the placebo group, the NYHA class improved in 3 percent of participants. The p-value was exactly 0.05.
Click on the figures and the table below for a larger version.
Mechanism
Conclusion
"Melatonin, by increasing psychologic parameters and cardiac potency, could be advised as a novel drug for treatment and palliating heart failure patients," the researchers write.


![According to an unpublished epidemiological study, presented in October 2025 at a conference of the American Heart Association, melatonin supplementation may increase the risk of heart failure. [sciencedaily.com November 4, 2025] We doubt whether that's actually true. Trials have shown that melatonin supplementation actually has a positive effect on heart failure.](plaatjes/melatonin-structure-large.gif)


