|
Omega-3 fatty acids sabotage breast cancer cells by boosting free radicals
If you ingest carotenoids such as beta-carotene through regular foods, they inhibit cancer. In breast cancer cells, this happens in a way that suggests that omega-3 fatty acids can enhance the cancer-inhibiting effect of carotenoids, we wrote a few days earlier. Beta-carotene makes cancer cells produce more receptors with which omega-3 fatty acids can interact, and increase the activity of free radicals in the cancer cells. But what exactly do omega-3 fatty acids with breast cancer cells when no carotenoids are involved?
Omega-3 fatty acids & cancer
A relatively high intake of omega-3 fatty acids appears to reduce the risk of breast cancer. In women who have had breast cancer, a diet with many omega-3 fatty acids reduces the chance of the disease recurring. How could that be?
In vitro study
A possible answer to that question can be found in an in vitro study that researchers at the University of Kansas Medical Center published in 2010 in PLoS One. The researchers exposed 3 types of cancer cells in test tubes to the omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA. These were hormone-sensitive MCF-7 breast cancer cells, hormone-insensitive MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells and MDA-MB-435s cells.
The last cell line is one with a complex history. For many years oncologists have considered him a strange type of breast cancer cell, but later it turned out to be a melanoma cell.
Whatever. Omega-3 fatty acids killed all cell types. The most effective cancer inhibitor was DHA. The most sensitive cell type were the MCF-7 cells.

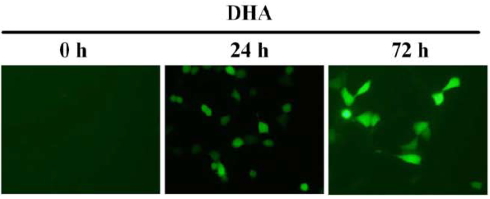
When the researchers in MCF-7 cells exposed to DHA looked at the reactive oxygen species formation - say: free radicals - they saw that DHA increased the concentration of these agressive molecules [above].
If free radicals can explain how DHA can kill cancer cells, this effect should disappear if you expose breast cancer cells not only to DHA, but also to hefty concentrations of antioxidants such as vitamins C and E and N-acetylcysteine.
And look at that.

DHA stimulated the activity of the suicide enzyme caspase-8, the researchers discovered.
Animal study
The researchers also did an animal study in which they implanted MCF-7 cells in mice and then watched how fast the tumors grew. If the mice also received fish oil through their food, the tumors grew significantly less rapidly. If the mice had been humans, they would have received 3-5 grams of fish oil a day.

The researchers repeated the experiment with mice into which they had implanted MDA-MB-435s cells. They achieved the same results. [Figure]
Conclusion
Our idea that omega-3 fatty acids and carotenoids enhance each other's cancer-inhibiting effect is not at all unlikely, although we have only looked at beta-carotene up to now. What about other carotenoids?
More coming soon.
Source:
PLoS One. 2010 Apr 22;5(4):e10296.
More:
Animal study: anti-cancer effect EPA and DHA 8 times greater than that of ALA 28.01.2018
Alpha-linolenic acid, the broad-spectrum breast cancer cell slayer 07.01.2018
Less omega-6, more omega-3, less breast cancer 24.12.2017
Archives:
Cancer Prevention & Survival
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Breast Cancer
Carotenoids
|








