|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
04.08.2025 |
|
|
More magnesium, younger brains
If your diet provides a relatively high intake of magnesium, the aging of your brain tends to slow down. Even if your magnesium intake is already perfectly aligned with official guidelines, an extra dose of magnesium may still contribute to preserving your cognitive health.
Study
The study participants had no known neurological or psychiatric complaints.
Whether the participants used magnesium supplements is unknown. The questionnaires the participants completed did not account for supplements. Therefore, the study participants with a high intake consumed a lot of products such as dark green leafy vegetables like spinach, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
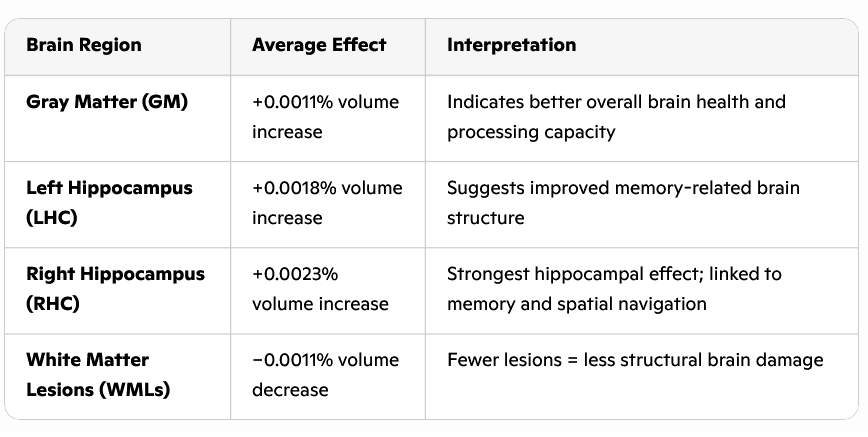
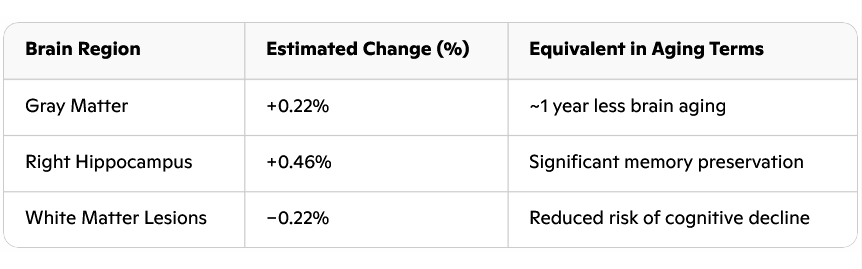
Results
Click on the tables for a larger version.
Now, if you're getting 350 milligrams daily, you're already doing great according to current guidelines. But if you add another 200 milligrams, you might actually slow down the aging of your brain. The effect on your gray matter - that's the part of your brain that processes info, stores memories, regulates emotions, and keeps your body moving - is roughly equivalent to making your brain one year younger.
Mechanism
Therefore, the researchers believe that magnesium primarily slows brain aging by lowering CRP levels and other inflammatory markers. [Eur J Nutr. 2024 Aug;63(5):1807-18.]
Benefits of more magnesium?
Source: More: Archives:
|
|
||||||||||||||||