|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
02.03.2015 |
|
|
Supplement with lactic acid and caffeine makes athletes' muscles bigger
If you and I even vaguely resemble the lab rats that sports scientists at Ritsumeikan University in Japan use for their experiments, then it would seem that we can build up more muscle by taking a supplement that contains lactic acid and caffeine. Sounds pretty crazy? Not after reading the fascinating article the Japanese published in the Journal of Applied Physiology.
In-vitro study
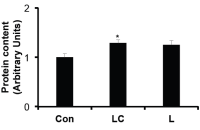
The figures below show that the combined exposure to lactate and caffeine boosted the synthesis of the anabolic signal proteins MyoD [below left] and myogenin [below right].
The combination of lactate and caffeine also activated the anabolic signal molecules mTOR [above left] and S6K [above right].
Animal study
The rats in the control group did not run and didn't get a supplement either.
The rats that got supplements were given them daily. If you convert the dosages to human proportions you arrive at about 10-14 g sodium lactate and 400-600 mg caffeine a day. The supplements were administered orally to the rats.
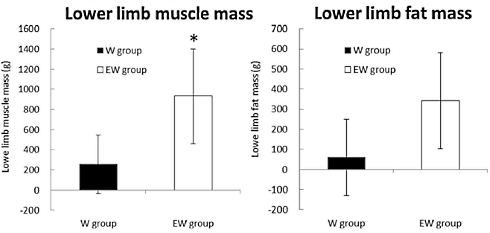
At the end of the four weeks the rats that had been given lactic acid and caffeine had built up more muscles than the animals that had only done exercise.
The researchers found that the rats that had been given the supplement had more DNA in their muscles. That suggests that the muscles had attracted more stem cells, which they had then changed into muscle cells.
Mechanism
"Lactate may activate calcium/calmodulin-activated serine-threonine phosphatases calcineurine and myogenin. Calcineurine dephosphorylates nuclear factor of activated T cell (NFAT). Calcineurine/NFAT is implicated in the regulation of satellite cell proliferation. Moreover, calcineurine/NFAT increases myogenic factor 5 (Myf5) expression, which is in the muscle regulatory factor family."
"Caffeine is an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase, increasing intracellular cAMP and actually activating the protein kinase cascade driven by cAMP (including Akt) in this study."
"Lactate and caffeine may complement one another to promote muscle anabolism and could effectively increase muscle mass by increasing satellite cell activity and anabolic signals."
Conclusion
"These results suggest that administration of lactate-caffeine compound could effectively increase muscle mass concomitant with elevated myonuclei, even with low-intensity exercise, by means of activated satellite cells and anabolic signals in skeletal muscle. Therefore, study of lactate-caffeine compound should provide insight into the development of strategies against muscle wasting and loss of function associated with a wide range of neuromuscular diseases such as sarcopenia."
Source: More: Archives:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||