|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
08.02.2013 |
|
|
Melissa officinalis is a smart drug
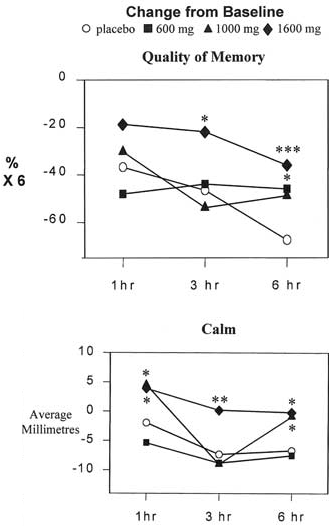
The brain works better after a single high dose of Melissa officinalis. The memory function improves, discovered psychologists at Northumbria University. Melissa officinalis, better known as lemon balm and available over the counter, is a legal smart drug.
Melissa officinalis

The memory-stimulating aspect of Melissa officinalis has long been ignored however. Melissa officinalis is still easy to buy in the form of tea, herb or supplement, but the claim most often made is that the herb calms the digestive system or helps users to fall asleep. The British researchers studied the other aspects of lemon balm [Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002 Jul; 72(4): 953-64.] after having done research on other herbs including ginseng [Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003 Jun; 75(3): 687-700.] and ginkgo [Nutr Neurosci. 2001; 4(5): 399-412.].
Study
The researchers then gave the students words, numbers and pictures to look at. The students then had to try and recall these six hours later.
Results
The subjects were also asked to indicate on a scale how calm they were feeling. From this the researchers discovered that the 1600-mg dose had a noticeable effect.
Mechanism
The Brits suspect that Melissa officinalis contains substances that can help fight Alzheimer's.
Source:
More: Archives:
|
|
|||||||||||||||