|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
17.02.2012 |
|
|
Animal study: vitamin C and E good for older strength athletes
The muscles of older rats that follow a modest strength-training programme are stronger if the animals are given extra vitamin C and E with their food, sports scientists at West Virginia University discovered.
Vitamins C and E are antioxidants. If you give them to young athletes they can inhibit positive training effects, such as increased insulin sensitivity and post-training muscle recovery, [Br J Nutr. 2006 May;95(5):976-81.] according to some studies. Other studies, however, suggest that the same vitamins actually have a positive effect on older athletes. Antioxidant supplementation enhances recovery in the muscles cells of older rats, and human studies show that elderly athletes build more muscle from their strength training if they take extra vitamin C and E.
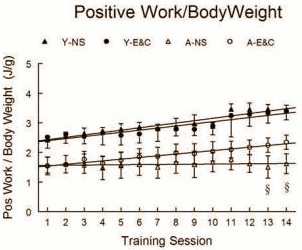
In 2010 American researchers published the results of an animal study in which they trained the dorsiflexors in rats' paws three times a week using a spring. The researchers used electrical stimuli to make the muscle contract [Repetitive loading]. The programme lasted just five weeks. The rats in the control groups did no training [Control].
Half of the rats were three months old [Young]; the other half were 30 months [Aged]. In both age groups, half of the animals were given standard animal feed [NS], and the other half were given food containing extra vitamin C and E [Vit E&C].
The supplementation had no effect on the circumference of the trained muscle in the elderly rats. But the strength with which these rats extended the spring increased with supplementation. To be more precise: the rats were capable of developing more power when they extended the muscle [Positive work]. Supplementation had no effect on the strength with which the rats were able to resist the spring as it returned to its original shape [Negative work].
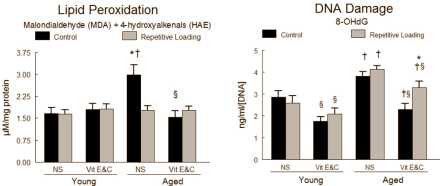
Supplementation reduced free-radical damage to the DNA in the muscles of the elderly rats that did training. The researchers suspect that this is because the vitamins activate endogenous protective enzymes. But to be honest the effects they report are very slight. We wonder if the mechanism doesn't work differently.
"Additional studies are required to determine if skeletal muscles in elderly humans who supplement their diet with Vitamin E and C during chronic resistance types of muscle loading, will respond in a similar fashion to the rodents in the current study", the Americans conclude. They emphasise that review studies show that supplements containing antioxidant compounds such as vitamin A, beta-carotene and selenium have more negative than positive effects.
The research was funded by the American government.
Source:
More:
|
|