|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
27.09.2012 |
|
|
Tryptophan helps lift interval training to a higher level
Tryptophan & exercise
Tryptophan is a precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin. If you have more serotonin in your brain than normal, you feel pleasanter. Your brain becomes less sensitive to pain and you will be less distracted by unpleasant thoughts and irrelevant information. So tryptophan supplementation can create a state of mind that also helps to improve sports performance.
Contradicting studies
Dutch researchers in the mid-nineties also recorded no effect. They gave their subjects tryptophan not before but during their physical exertion. [J Physiol. 1995 Aug 1;486 (Pt 3):789-94.]
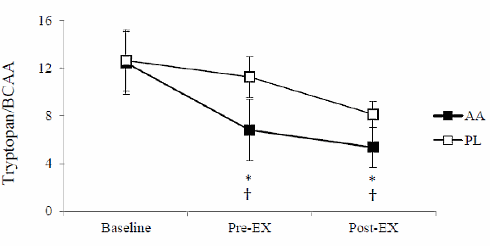
But the people who are most resistant to the idea that tryptophan may enhance sports performance are researchers who believe in the enhancing effect of BCAAs. These amino acids, according to a widely accepted theory, reduce fatigue during endurance exertion because they prevent tryptophan from entering the brain, thereby preventing it from being converted into serotonin. [Experientia. 1996 May 15;52(5):413-5.] [J Nutr. 2006 Jan;136(1 Suppl):274S-6S.] [J Nutr. 2006 Feb;136(2):544S-547S.]
The brain can only absorb a limited amount of amino acids, according to theory. During intensive physical exercise the muscles claim all amino acids from the blood – except for tryptophan. As a result the brain absorbs more tryptophan and converts this into serotonin - and serotonin causes athletes to feel tired.
BCAA supplementation inhibits the brain's uptake of tryptophan, reduces fatigue and boosts endurance performance, whereas tryptophan supplementation only leads to negative effects, say BCAA supporters.
Study
First the students cycled for 10 minutes at 50 percent of their VO2max. Then they cycled flat out for 30 seconds. The subjects had to repeat this cycle another three times. And finally the students cycled for another 20 minutes at 50 percent of their VO2max.
The researchers performed the test twice. On one occasion the students took 2 capsules containing 300 mg tryptophan for three days before the test and on the day of the test itself, so they took 600 mg tryptophan per day. On the day of the test the students took the tryptophan two hours before starting to cycle.
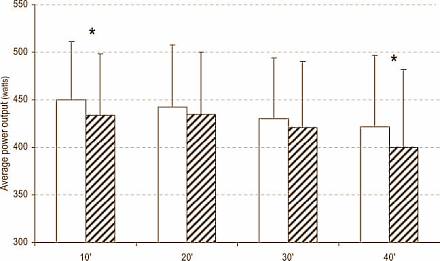
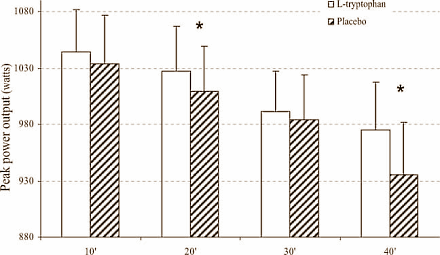
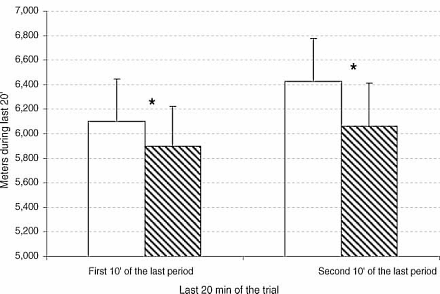
Results
The researchers discovered that tryptophan supplementation reduced the increase in fatigue.
In the experiments where tryptophan did not have an effect it's possible that too high a dose of tryptophan was used, or that it was not given sufficiently in advance of the exertion. The researchers suggest that tryptophan is perhaps not only a precursor of serotonin, but also of related compounds that do not cause fatigue but may actually have a stimulatory effect.
Conclusion
Supplements manufacturer Recuperation Electrolitos funded the research.
Source:
More:
Archives:
|
|
|||||||||||||||||