|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
25.07.2019 |
|
|
The modest fat loss effect of chlorogenic acid
Study
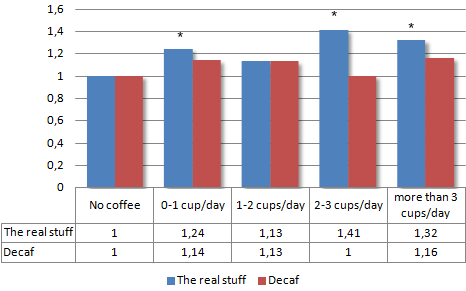
Besides caffeine, chlorogenic acid analogues are the most important bioactive constituents of coffee. They are also the most important ingredients in the Green Coffee Bean extracts that you find in all kinds of weight loss supplements, and which, according to some fraudulent studies, could lead to 8 kilos of weight loss.
Results
Click on the figures below for a larger version.
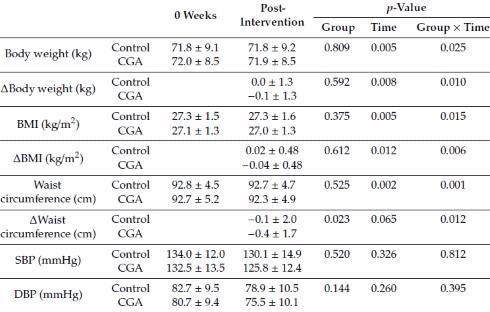
According to abdominal scans, the subjects in the experimental group had slightly less belly fat after the trial. This effect was statistically stronger than the one above, but still modest.
Mechanism
"According to a human clinical trial comparing daily consumption of roasted coffee containing 359 mg chlorogenic acids and placebo coffee for one week, repeated consumption of chlorogenic acids decreased the respiratory quotient and increased oxygen consumption, which means that both energy expenditure and fat oxidation were increased." [J. Health. Sci. 2010, 56, 745-51.]
"Furthermore, feeding green coffee bean extract containing chlorogenic acids to mice with diet-induced obesity affects body fat accumulation, with a dose-dependent inhibition of the increase in body weight and accumulation of visceral fat and liver fat." [Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jan;300(1):E122-33.]
"In addition, analysis of the expression of energy metabolism-related genes in the liver revealed significantly decreased messenger RNA expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1, acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), and ACC2, which are involved in fatty-acid oxidation, after mice were administered green coffee bean extract containing chlorogenic acids for two weeks."
"Decreased expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 and ACC1, which are involved in fatty-acid synthesis, promotes energy expenditure, and decreased ACC2 expression increases fatty-acid oxidation in the mitochondria through the reduced production of malonyl CoA, which inhibits carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1."
Conclusion
Source: More: Archives:
|
|
|||||||||||||||||