|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
26.08.2010 |
|
|
Sprint training works better on a hill
Some of the students only trained uphill [U]. Others trained only downhill [D]. Yet another group trained on the horizontal [H], and the last group trained both uphill and downhill [U+D].
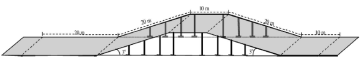
Paradisis used an artificial hill for the training, shown above. To give you an idea: the test subjects in the U+D group ran from left to right and covered a total distance of 80 metres. The uphill and downhill slopes of the hill had a gradient of 3 degrees.
At the end of the 6 weeks, the maximum speed [MRS] the students developed had increased most in the U+D group. This was mainly because the students had increased the number of steps per second they could take. Their step rate [SR] had increased.
Paradisis suspects that the sudden transition from uphill to downhill running is the main factor in the success of the U+D training.
"During uphill running, participants experienced a resistive stimulus, followed by a normal stimulus (horizontal), and then a facilitative stimulus (downhill)", the researcher writes.
"During the first stimulus, the neuromuscular system was overloaded, whereas immediately afterward it was progressively unloaded (horizontal - downhill). It seems that this rapid transition from the first stimulus to the second, from overloaded to facilitative, benefited the neuromuscular system. The immediate transition from the overload status to the facilitated status seems to be the key factor to the training adaptation."
Source:
More:
|
|