|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
31.07.2015 |
|
|
Short-term magnesium supplementation boosts maximal strength
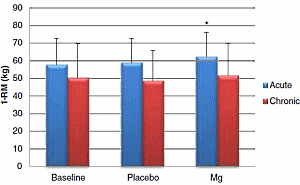
Magnesium supplementation makes you stronger, but the effect depends on how long you use it for. Lindsy Kass and Filipe Poeira of the University of Hertfordshire write in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition that only short periods of magnesium supplementation boost maximal strength. If you take magnesium for weeks on end it'll have no effect on your strength.
Magnesium
The study that Kass and Poeira recently published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition confirms the findings of the earlier study. But the researchers discovered another, and possibly even more interesting effect of magnesium supplementation.
Study
The other half took a magnesium supplement for four weeks [Chronic], and on another occasion was given a placebo for four weeks.
Results
The researchers suspect that magnesium supplementation has a performance enhancing effect, but that this effect disappears after a couple of days "perhaps due to saturation of Mg2+ within the blood or limitations to transporters."
The blood-pressure reducing effect of magnesium supplementation did continue throughout the longer-term supplementation.
Conclusion
It's not clear to what extent the findings also apply to strength athletes. The subjects were not used to weight training and before they did the bench presses they'd already cycled 40 km.
Source:
More:
|
|