|
High doses of vitamin C and E may undermine effect of endurance and interval training
High doses of vitamin C and E have a negative effect on the results of endurance training, according to a human study that researchers at the Norwegian School of Sport Sciences published in the Journal of Physiology.
Study
The researchers performed an experiment on 54 fit students, of whom most did running or cycling in their free time. The subjects followed a training programme consisting of continuous sessions of 30 and 60 minutes and interval training consisting of four-minute sets. They did this for a period of 11 weeks.
Half of the subjects took a supplement containing 500 mg vitamin C and 117 mg vitamin E [in the form of DL-alpha-tocopherol acetate] just before and just after each session. So the subjects took a total of 1000 mg vitamin C and 234 mg vitamin E daily.
The other half of the subjects took a placebo.
Results
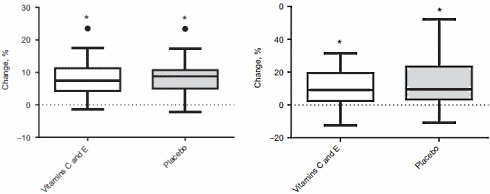
The researchers also recorded the subjects' maximal oxygen uptake at the beginning and end of the 11 weeks. The figure on the left below shows that the increase in VO2max was the same in the placebo group and in the supplement user group.
The researchers also measured the subjects' endurance capacity by getting them to do the 20 m shuttle run test or the beep test. The figure on the right below shows that supplementation had no influence on this either.
But the researchers did notice effects of the supplementation when they examined the subjects' muscles. The figure on the left below shows that the gene for PGC-1-alpha was more active in the supplements users. At first glance that would appear to be a beneficial result. PGC-1-alpha is a transcription factor that plays a key role in the manufacture and functioning of mitochondria in muscle cells. More mitochondria = more endurance capacity.
But the researchers found less PGC-1-alpha in the cytosol of the cells of the supplements users [figure on the right below]. The PGC-1-alpha gene does work harder as a result of supplementation, but nevertheless that leads to less PGC-1-alpha, and therefore in the long term probably fewer mitochondria and less endurance capacity.

Conclusion
"Supplementation with high dosages of vitamin C and E appears to diminish some of the endurance training-induced adaptations in human skeletal muscles", the researchers summarised. "We suggest that high dosages of isolated antioxidants should be used with caution in individuals who are simultaneously engaged in endurance training."
Source:
J Physiol. 2014 Apr 15;592(Pt 8):1887-901.
More:
Vitamin C negates effects of endurance training 23.08.2010
High doses vitamin C and E buffer cardio effect on fat rolls 27.05.2009
Archives:
Vitamin C
Vitamin E
|


