|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
07.08.2015 |
|
|
Fructose makes you extra fat because it makes you lazy too
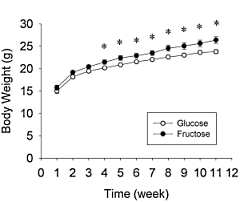
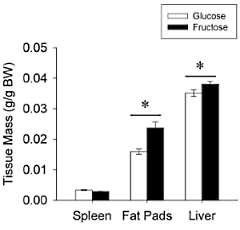
If you consume large amounts of sugar you'll not only get fatter, you'll also get fatter faster than if you consume large amounts of glucose. That's because fructose – one of the components of sugar – makes you lazy, which means you move less. Nutritionists at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign discovered this when they studied the effect of a high-fructose diet on mice.
Glucose, fructose and sugar
Fructose is a component of sucrose, ordinary sugar, but an increasing number of foods also contain fructose alone. Fructose is a component, for example, of High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS).
Researchers like Robert Lustig have been warning for years about the consequences of a high fructose intake. Fructose doesn't convert easily into glucose. It's glucose that stimulates the production of insulin, the hormone that induces cells to absorb glucose.
With fructose the process doesn't go so smoothly, so fructose tends to hang around more in the bloodstream. As a result, a diet that contains a lot of fructose is more likely to lead to diabetes, cardiovascular disease and overweight than a diet that contains a lot of glucose.
The animal study done at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, which was recently published in Scientific Reports, confirms the dangers of our current intake levels of fructose.
Study
Results
The researchers used cameras to monitor how much the mice moved around in their cages at night [mice are nocturnal animals]. They observed that the mice in both groups started to move less when the experiment began. But the decrease in movement was bigger in the fructose group than in the glucose group.


Conclusion
"Such changes in energy expenditure are likely to have important implications in regard to regulation of body weight and energy balance in long-term consumption of fructose. It is realistic to consider an increase in physical activity as a way to ablate the potential negative impact of fructose consumption in body weight."
Source:
More:
|
|