|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
05.10.2013 |
|
|
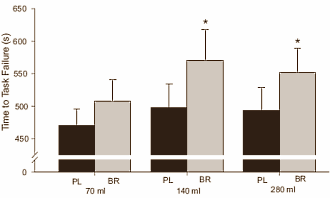
Concentrated beetroot juice: optimal dose is 140 ml
Beetroot juice contains nitrate, a precursor of nitrogen monoxide, a signal substance that widens the arteries, thus boosting the supply of oxygen and nutrients to muscle cells – and probably enhancing athletic performance in other ways too. Studies show that nitrogen donor supplementation helps muscle cells to use oxygen more efficiently during bursts of intensive exercise. It seems that preparations such as beetroot juice help make cells' energy metabolism more efficient.
Despite the impressive amount of scientific evidence for the performance-enhancing effect of beetroot products, there were no dose-response studies until now. Thanks to these sports scientists we now have one. The product they used for their experiments was Beet-It.
The researchers got their subjects to pedal increasingly intensively on a cyclometer. They recorded how long they managed to cycle for before giving up. The figure below shows that a dose of 140 ml concentrated beetroot juice enabled the students to keep going for a significantly longer amount of time.
This was also the case when the intake was 280 ml, but the students didn't perform any better after taking 280 ml beetroot juice than they did after taking 140 ml.
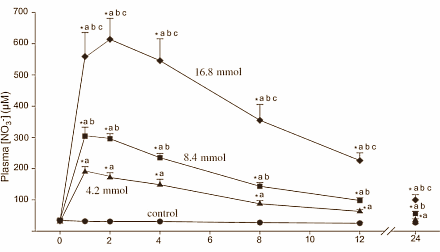
After taking 280 ml beetroot juice, the subjects' concentration of nitrate in their blood did rise by more than when they took 140 ml. This was not the case for the nitrite concentration.
The subjects' resting blood pressure went down after consuming the concentrated beetroot juice. The figure below shows that the effect on systolic blood pressure was not significantly greater at the 280 ml dose than at the 140 ml dose.
So most athletes are likely to derive optimum benefit at a dose of 140 ml and it's unlikely that higher doses will further improve their performance. Note, 'most' is not the same as 'all'.
"In terms of positive changes in time-to-task failure, there were three nonresponders in the 4.2-mmol condition, two in the 8.4-mmol condition, and one in the 16.8-mmol condition", the researchers write. "Individual subjects who did not respond at lower doses did respond at higher doses."
No side effects were observed although the subjects did report that their urine and stools were red.
Source:
More:
|
|