|
Cinnamon boosts IGF-1, rejuvenates skin
A cinnamon supplement can help against skin aging, conclude biochemists at Osaka Prefecture University in Japan from a study in which they exposed skin cells to extracts of ten edible herbs in test tubes.
Young skin, collagen & IGF-1
If you're a supplements or cosmetics manufacturer looking for products to reduce skin aging, there are two factors you need to take into account: collagen and IGF-1. Skin owes its suppleness and youthfulness to a high level of collagen synthesis by the skin cells, and the hormone that stimulates the skin cells to produce collagen is IGF-1.
Study
There are indications that molecules in our food can enhance the effect of insulin – which in many respects resembles the effect of IGF-1. That's why these researchers wondered whether they could find these molecules in edible herbs.
Results
When the Japanese exposed skin cells to ten different herb extracts in test tubes, they noticed that fenugreek, cinnamon and Iranian cumin in particular boosted collagen production. The bigger the blob in the figure below, the greater the collagen synthesis.

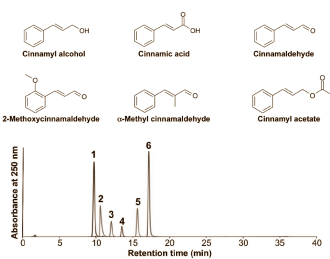
Cinnamon from Sri Lanka boosted the collagen production the most, the researchers discovered. HPLC analysis revealed the following compounds, as shown in the graph above: peak 1 = cinnamyl alcohol; peak 2 = cinnamic acid; peak 3 = cinnamaldehyde; peak 4 = 2-methoxycinnamaldehyde; peak 5 = alpha-methyl cinnamaldehyde; peak 6 = cinnamyl acetate.
Cinnamaldehyde in particular enhanced collagen synthesis, the researchers discovered.

Mechanism
Cinnamaldehyde improves the performance of IGF-1, the researchers discovered. They discovered more phosphorylated IGF-1 receptors in skin cells that had been exposed to IGF-1 rather than to cinnamaldehyde. So cinnamaldehyde doesn't lead to the creation of more IGF-1 receptors, but does ensure that, once IGF-1 has attached itself to its receptor, that the signal is transmitted better to the cell.
The same actually also happened in experiments without IGF-1, so it would seem that cinnamaldehyde can replace IGF-1 in skin cells. [Hmm... If cinnamaldehyde does the same in muscle cells...]
Conclusion
"Our findings could be helpful in improving the signs and symptoms of aging skin since a reduction in dermal collagen production is considered to be its principal cause", the researchers conclude. "The mechanism by which cinnamaldehyde induces the ligand-independent activation of IGF-I receptor will be addressed further in the near future."
Source:
J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Feb 8;60(5):1193-200.
More:
Cinnamon fights migraines 04.08.2020
Cinnamon extract supplement boosts muscle mass 19.11.2015
Cinnamon piles the glucose on in the muscles 09.02.2011
Archives:
Beautyceuticals
Cinnamon
|