|
Caffeine increases calorie consumption by physical exercise
If you exercise more, your fat percentage will probably decrease. This effect is further enhanced if you exercise with a decent amount of caffeine in your system. This is evident from an animal study that researchers from Kent State University in the US will shortly publish in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology.
Study
The researchers had lab rats run for 25 minutes on a treadmill. Twenty minutes before the session started, the researchers gave a group of animals a dose of coffee. The human equivalent of the dose was somewhere between 400 and 800 milligrams.
Another group of rats received a placebo.
Results
Caffeine supplementation allowed the rats to consume more energy on the treadmill. Significantly, that effect only became apparent after 25 minutes.
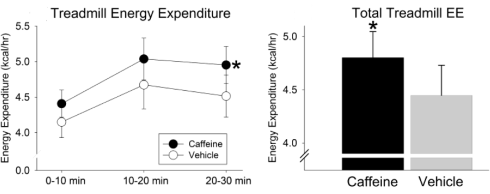
According to sensors that the researchers had stuck on the rats, during exercise the rats' muscles produced more heat when they had been given caffeine. This explains the increased calorie consumption by exercise: the active muscles use more energy because they release more heat.


Conclusion & mechanism
"Altogether, this study demonstrates that caffeine decreases fuel economy or physical activity, increasing the caloric cost of activity even when activity level or workload is constant", the researchers summarize their results. "This is accompanied by an amplification of muscle thermogenesis, but only after 25 min of treadmill walking."
"This increase in calorie use may partly underlie the known ability of caffeine to induce weight loss or prevent weight gain in laboratory animals and promote negative energy balance in humans."
"Similar to the ability of caffeine to enhance athletic performance, the metabolic effects reported here may occur through multiple mechanisms, including elevated sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATP-ase activity secondary to caffeine's increase of RYR-induced sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATP-ase and an associated protein, sarcolipin, have been implicated in skeletal muscle thermogenesis, generating heat at the expense of ATP."
"The potential role of Ca2+ cycling in economy of physical activity is supported by the association between sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATP-ase and enhanced muscle work efficiency seen during weight loss-induced adaptive thermogenesis in humans."
Source:
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019 Jan 8. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13065. [Epub ahead of print].
More:
Speed up interval-training fat loss with supplement containing caffeine and green tea 19.01.2016
Green tea boosts fat burning after interval training 30.10.2015
In vitro study: caffeine + quercetin + exercise = enhanced fat loss 04.09.2009
Archives:
Weight Loss Supplements
Weight Loss
Caffeine
|