|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
11.09.2010 |
|
|
Bodybuilding effects of arginine-alpha-ketoglutarate modest at best
Arginine, citrulline and other NO precursors are of interest to strength athletes, but not all arginine products are equally convincing in studies. Take arginine alpha-ketoglutarate: AAKG was found to have some effect in a study done at Baylor University, but bodybuilders may be better off spending their money on other things.
Pretty promising you might think. Indeed, studies have shown that a mix of citrulline and malate lives up this promise, and there are also indications that a mix of arginine and aspartate has interesting ergogenic effects. But arginine and alpha-ketoglutarate? Well...
The researchers gave their male subjects, all experienced weight trainers aged between 30 and 50, 12 g AAKG every day for 8 weeks. The men divided their intake over three moments throughout the day. The capsules they took contained equal amounts of arginine and alpha-ketoglutarate. A control group trained, but were given a placebo.
The subjects trained 4 times a week, exercising each muscle group twice a week. The control group and the AAKG group had identical training programmes and diet. The training sessions consisted of 2 chest exercises, 2 for the back, 1 for the shoulders, 1 for the biceps, 1 for the triceps, 1 for the stomach, 2 for the quadriceps, 2 for the hamstrings, 1 for the calves and 1 for the lower back.
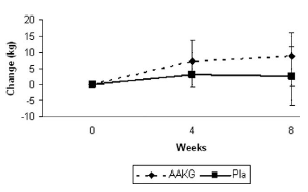
After 4 and 8 weeks, the researchers observed that the subjects in the AAKG group had made more progress with the bench press. The weight at which the AAKG group subjects could just manage 1 rep for the bench press had increased by 9 kg by the end of the period. In the control group the weight increase was 3 kg.
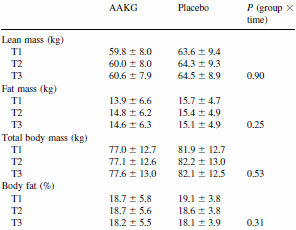
AAKG had no effect on body composition, as the table above shows.
The researchers also looked at whether AAKG improved the subjects' aerobic performance on the cardio equipment. It didn't.
Reading between the lines it looks like the researchers find the results disappointing, although they reserve judgement on AAKG. "Further research is needed to examine the role of AAKG supplementation during training in untrained and trained populations before definitive conclusions can be drawn regarding its potential ergogenic value."
Source:
More:
|
|