|
Lengthy cardio training stimulates growth hormone secretion more than strength training does
The results of a human study that researchers at the US Army Research Institute of Environmental Medicine will soon publish in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise fly in the face of the message found in nearly all popular articles on exercise, health and hormones. But because we know that our readers weren't born yesterday, we've written about it. According to the researchers, two hours of cardio training boosts your body's growth hormone secretion more than doing one or two hours of strength training.
Ways of optimising your endogenous production of growth hormone are of particular interest to life extenders because growth hormone helps to restore muscle fibre, bone, cartilage and skin. But growth hormone is also of interest to people who want to lose fat. Growth hormone pulses stimulate muscle cells to burn fat.
Study
Intensive exercise stimulates the secretion of growth hormone, according to many studies. But most of these only measure growth hormone secretion during the first few hours after an exercise session. No studies had ever been done that measured the effect over a 24-hour period, and that compared the effect of different kinds of exercise. So these researchers decided to fill this gap.
The researchers got eight male recreational athletes who were in their twenties to do on different occasions: a) nothing [Control], b) an hour of strength training using weights with which they could manage 5-10 reps [Moderate strength training], c) two hours of strength training [Long strength training], d) an hour of cycling at 70 percent of VO2max [Moderate aerobic training] or e) two hours of cycling [Long aerobic training].
The strength training session consisted of squats, bench presses, leg presses and lat pull-downs; the cardio training consisted of 15-min sessions with a couple of minutes rest in between.
Results
The figure below shows that over a period of 20 hours both the Moderate strength training and the Moderate aerobic training boosted the amount of growth hormone in the blood compared with doing nothing. But the increase in these cases was not statistically significant. The increase in the amount of growth hormone in the blood after the Long aerobic training was significant.
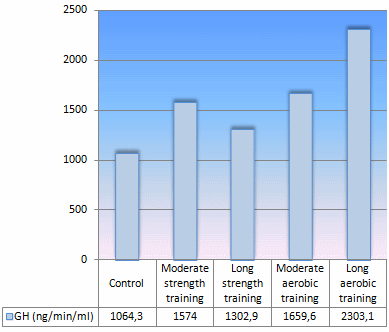

The figures above show the amount of growth hormone in the blood of one of the participants. LA = Long aerobic training; MA = Moderate strength training.
Conclusion
The researchers are aware that textbooks and the popular media usually say that it's strength training that boosts growth hormone secretion and that their study showed unexpected results.
"We believe that the underlying cause may be due to the greater energy expenditure achieved during aerobic exercise and a greater demand for post-exercise fat mobilization", the researchers write. "The physiological significance of GH pulsatile secretion and its important metabolic role with regard to fuel provision are further reinforced by the recent findings of Surya et al. [J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Aug;94(8):2828-34.] who reported that only pulsatile, not continuous, delivery of GH stimulates lipolysis in humans."
Source:
Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014 Feb 26. [Epub ahead of print].
More:
Squat produces more growth hormone and testosterone than leg press 09.01.2014
Animal study: eleven hundred percent more testosterone and three hundred percent more growth hormone with Rubus coreanus 16.09.2013
Extra high growth hormone peak with clever interval training 26.03.2013
|




