|
How to make training with light weights just as effective as training with heavy weights
If for any reason you can only train with light weights, you can still gain strength and build up muscle mass. According to researchers at the University of Tokyo you just have to move the weights more slowly.
Alternative approaches in strength training
Strength training is a medicine that is good for almost everything, but not everyone can do strength training in the regular way. For example, 20 percent of the over 70s develop joint and muscle problems if they train using their maximal weight, and doctors are not sure that the rise in blood pressure and heart rate caused by regular strength training is good for people with cardiovascular problems.
You can solve these problems by training not with 80 percent of your 1RM, but with 50 percent instead. But the text books tell us that this level of strength training doesn't have as much effect. It's not without reason that bodybuilders train at 80-85 percent of their 1RM.
One alternative that the researchers at the University of Tokyo have been testing is to train with extremely short pauses between sets – just 30 seconds, for example. Studies have shown that if you do strength training with 50 percent of your maximal weight in this way it does result in an increase in muscle strength and mass. [J Strength Cond Res. 2002 Feb; 16(1): 123-8.]
Another alternative is the super-slow method, in which you take 10 seconds to do the concentric movement and 4 seconds to do the eccentric movement. Studies have shown that using this method with light weights still builds up mass and strength. [J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2001 Jun; 41(2): 154-8.]
Yet another alternative is kaatsu training - a form of strength training using light weights while restricting the blood supply to the muscle group being trained. The researchers are cautious about kaatsu training, as to use this method safely requires a thorough knowledge of it, which can't be gained from a bit of casual surfing.
Study
For this reason the researchers looked at yet another method, which they call 'resistance exercise with relatively slow movement and tonic force generation'. This involves training with 50 percent of your maximal weight, but moving so slowly that you can just manage to do 8 reps. The researchers decided to make both the concentric and eccentric movements take 3 seconds.
They got 24 male students to train their leg muscles on a leg-extension machine three times a week for 12 weeks. The students were divided into three groups, and each group trained in a different way.
The LST group was the experimental group and they did 'resistance exercise with relatively slow movement and tonic force generation'.
The HN group was the first control group. These students trained in the usual way, performing sets of 8 reps at 80 percent of their maximal weight.
The LN group was the second control group. The students in this group trained in the usual way, performing sets of 8 reps at 50 percent of their maximal weight. Unlike the other two groups, the LN group students did not train to failure.
Results
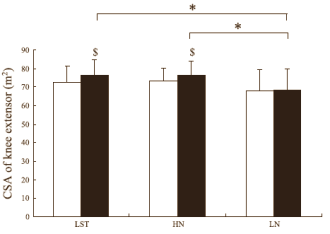
The researchers discovered that the LST group made almost as much progression as the HN group. The maximal strength in the LST group increased by 28 percent; in the HN and group the figure was 32 percent and in the LN group it was16 percent. The CSA – read muscle mass – increased by the same amount in the leg muscles of the LST and HN groups, whereas there was no increase at all in the LN group.

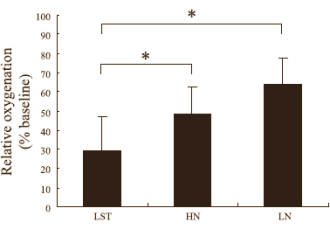
During the sets the amount of oxygen in the muscles of the LST group decreased dramatically. Despite the minimal weight used, this probably caused the concentration of lactic acid in the blood of the LST group to rise by as much as it did in the HN group.

Mechanism
The researchers suspect that the oxygen depletion in the muscle cells causes muscle enlargement. This isn't the only factor, but it is a pretty important one. Oxygen deficiency causes the concentration of lactic acid in the blood to rise, and as a result the synthesis of anabolic hormones such as growth hormone and testosterone also increases. In addition, oxygen deficiency causes a temporary increase in the activity of free radicals in the muscle cells, as a result of which the compensatory training results in more muscle build up.
Conclusion
"A low-intensity resistance exercise with slow movement and tonic force generation was effective for gaining muscular size and strength", the Japanese conclude. "This exercise was not associated with the generation of large force, so it would be useful for introductory strength training and rehabilitation from orthopedic injuries."
Source:
J Appl Physiol. 2006 Apr;100(4):1150-7.
More:
Higher growth hormone peak makes hypoxia-gym training more effective 29.03.2012
Bodybuilders grow five times faster in hypoxia gym 29.06.2011
Regular strength training more effective than Kaatsu training 31.03.2011
|





