|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
22.04.2014 |
|
|
Glucosamine, the life extender
Three signs
Secondly, it was published in Nature Communications, a scientific journal with an impact factor of just over 10. Nature Communications is in the top two percent of most influential scientific journals there are.
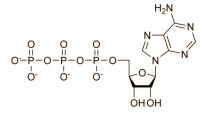
Glucosamine
They had already previously shown that compounds that inhibit carbohydrate metabolism, and also low-carb diets, can extend the lifespan of laboratory animals.
Study
Results
In the bar charts red also represents the animals that had been given glucosamine.
As a result of the disruption to the animals' metabolism, their mitochondria started to make more free radicals [such as hydrogen peroxide H2O2] after two days. The cells reacted to this by stepping up their production of endogenous antioxidants, such as the enzymes superoxide dismutase [SOD] and catalase. As a result of this the concentration of free radicals in the cell went down - and reduced the tempo of aging.
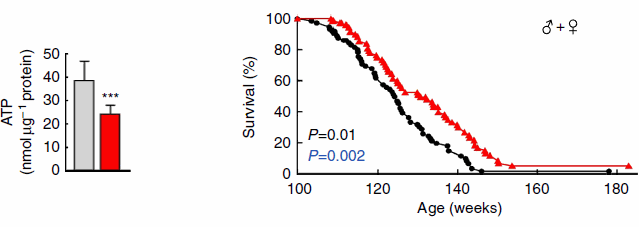
When the researchers gave mice glucosamine, they lived to be older than the mice that had not been given glucosamine.
The researchers mixed glucosamine into the animals' food from the age of 100 days. The human equivalent dose that they used is about 1g per 10 kg bodyweight per day. The type of glucosamine the researchers used is not revealed in the article.
The mice also produced less ATP when they were given glucosamine.
If the mice were given antioxidants such as N-acetylcysteine (NAC] or butylated hydroxyl anisole [BHA] the life-extending effect of glucosamine disappeared.
The mice that were given glucosamine started to burn more proteins. Glucosamine caused the cells to manufacture more receptors to absorb the amino acids. In mice where the receptors didn't work, glucosamine had no life extending effect. So it would seem there is a relationship between life extension through glucosamine and protein metabolism.
Conclusion
Source:
More:
Archives:
|
|
|||||||||||||||||