|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
28.01.2013 |
|
|
Ginsenoside-Rg1 in Panax ginseng protects athletes' muscles
Siberian ginseng is yet another story. In fact Siberian ginseng isn't ginseng at all.
The Taiwanese study, which was published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, is about ginsenoside-Rg1. The study is part of a bigger project. The same researchers recently also published the results of a study in which they describe how supplementation with ginsenoside-Rg1 during extreme physical exertion had a protective effect on the liver of lab animals. [Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012; 2012:932165.]
Ginsenoside-Rg1 is an interesting substance. In cell and animal studies it has been shown to boost the production of insulin receptors; it stimulates the creation of new blood vessels and wound healing; relaxes and widens blood vessels and lowers blood pressure. [Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008 Sep; 29(9): 1103-8.]
The roots of Panax ginseng can contain anywhere between 0.17 and 0.27 percent ginsenoside-Rg1. That doesn't sound like much, but the Taiwanese discovered that 0.1 mg per kg bodyweight is enough to have a strong effect. If you convert this quantity to the amount a human weighing 80 kg would need you arrive at 1.5 mg per day. To have that amount you'd only need several hundred milligrams of Panax ginseng per day.
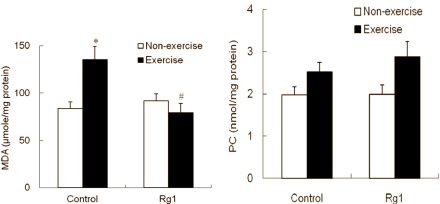
The activity of some antioxidants, such as glutathione peroxidase [GPx], was raised during rest, which may have offered the rats some protection during the first phase of exercise. The activity of other antioxidants, such as glutathione S-transferase [GST], was raised when the researchers fished the animals out of the water.
Ginsenoside-Rg1 lowered the concentration of malondialdehyde [MDA] in the muscles of the rats that had swum. That suggests that the muscle membranes had incurred less damage. The supplementation had no effect on the concentration of protein carbonyl [PC], a marker for damaged proteins.
"The study suggests that Rg1 can be used to design nutraceutical supplements aimed to preserve normal biomolecular structure of skeletal muscle against exhaustive exercise-induced oxidative stress, which might be important in preventing loss of cellular function and warrants quick recovery after sports competition", the Taiwanese conclude.
We suspect that the creation of such 'nutraceutical supplements' will require above all the efforts of production technologists. Much ginsenoside-Rg1 is lost in the traditional steaming process that is used to make ginseng-based preparations.
Source:
More:
|
|