|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
18.02.2010 |
|
|
Strength training helps back pain
Study
The programme lasted 16 weeks. Thirty men participated, of whom the 15 in the control group did no training.
For the first week the active group trained at 55 percent of the weight at which they were able to just do 1 rep (1RM). During the experiment the intensity was increased gradually up to the last week when the men trained at 79 percent of their 1RM. So the men did linear periodized training.
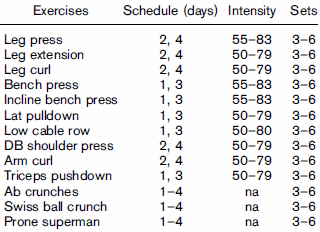
The subjects trained 4 times a week, taking 2 sessions to cover all muscle groups in the body. They took 1-2 minutes' rest between sets. They started out training as much as possible on machines, but as the experiment progressed they went over to free weights where possible. The table below shows the exercises the men did.
The researchers divided the men in the training group into 2 subgroups: a group with an average age of 52 [ME] and a group with an average age of 63 [OE]. They did this because they wanted to know whether older men react less well to strength training than younger ones.
Results
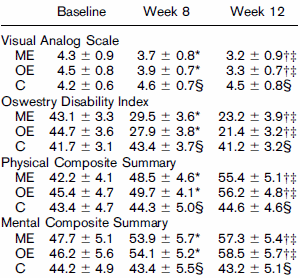
The Visual Analog Scale measures pain on a scale from 1-10. The lower the score, the less the pain.
The Oswestry Disability Index indicates to what extent people are capable of carrying out everyday activities. The scores range from 0-100. A score of 20-40 percent means you’re functioning, but have pain. A score of 40-60 percent means you are suffering from a good deal of pain and need to see a doctor.
The Physical Composite Summary and the Mental Composite Summary indicate your physical and mental state. The higher your scores, the better your quality of life. The scores range from 0 to 100.
The training programme was beneficial on all scores. When the researchers compared the effects for the two age groups, they found that the subjects in their sixties reacted as well as the subjects in their fifties.
Conclusion
Source:
More:
Archives:
|
|
||||||||||||||||